What is KYC (Know Your Customer) in Crypto: A Complete Guide to Verification

What is KYC and Why Does a Business Need It?
When using various trading platforms, users regularly encounter the need to undergo an identity verification procedure, or KYC. Previously, this requirement was not very common, especially in the crypto market, but today almost every platform asks to confirm your identity. If a user refuses, in most cases, the functionality of the platform on which they wanted to perform trading operations is significantly restricted. In some cases, using the platform at all will be impossible without KYC.
So what is KYC and why is it so important for trading platforms today? Let's break it down in this article.
Definition of KYC
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a set of rules and procedures that companies (usually from the financial sector) must perform to verify the identity of their clients in order to comply with the regulatory frameworks of local regulators. This concept was introduced to prevent money laundering and confirm the identity of a potential client.

In other words, KYC is the collection of information about the users of a financial platform to understand who will be using the site's services. Usually, when passing the identity verification procedure, it is required to provide the full name, date of birth, registration address, as well as a personal photo and a scan or photo of an identity document.
Why is KYC Verification Needed?
The identity verification procedure has a number of main tasks:
-
Combating financial crimes. Since the client discloses their identity, the platform can request detailed information about them from the databases of local regulators. Thus, if a user has already been noticed in illegal activities, the platform can alert the relevant authorities about their intentions or wait for transactions to be carried out in order to track them;
-
KYC today is a mandatory requirement for financial platforms in almost all countries of the world. Without compliance with this rule, a company will not be able to provide its services within the country;
-
Thanks to information received from local regulators, the platform can assess how profitable it is to provide a service to a given user. This helps minimize the risks of undesirable clients;
-
With the help of the identity verification procedure, platforms can more effectively set up internal business processes. KYC automates the collection and analysis of client data;
-
A platform with identity verification is initially more attractive to users. And we are talking not only about potential clients but also about regulators. In 2025, there is a distrustful attitude from both sides towards financial platforms where KYC is not implemented.
The KYC Process: Key Stages
Today, there is a standardized scheme for conducting the verification procedure:
-
Initial data collection. The platform must obtain the full name, date of birth, address, and an identification document from the user;
-
Afterward, the platform's specialists check the received data for authenticity: photographs are carefully studied, after which a conclusion is made whether the document is original or fake;
-
Next comes risk analysis. As already mentioned, a trading platform can request any information on a client from local regulators: credit history, litigation, possible links to criminal elements;
-
Confirmation of information. Here, the platform compares all information received from databases, thereby confirming its accuracy. If everything matches, the user passes the verification procedure and gains access to the platform's services.

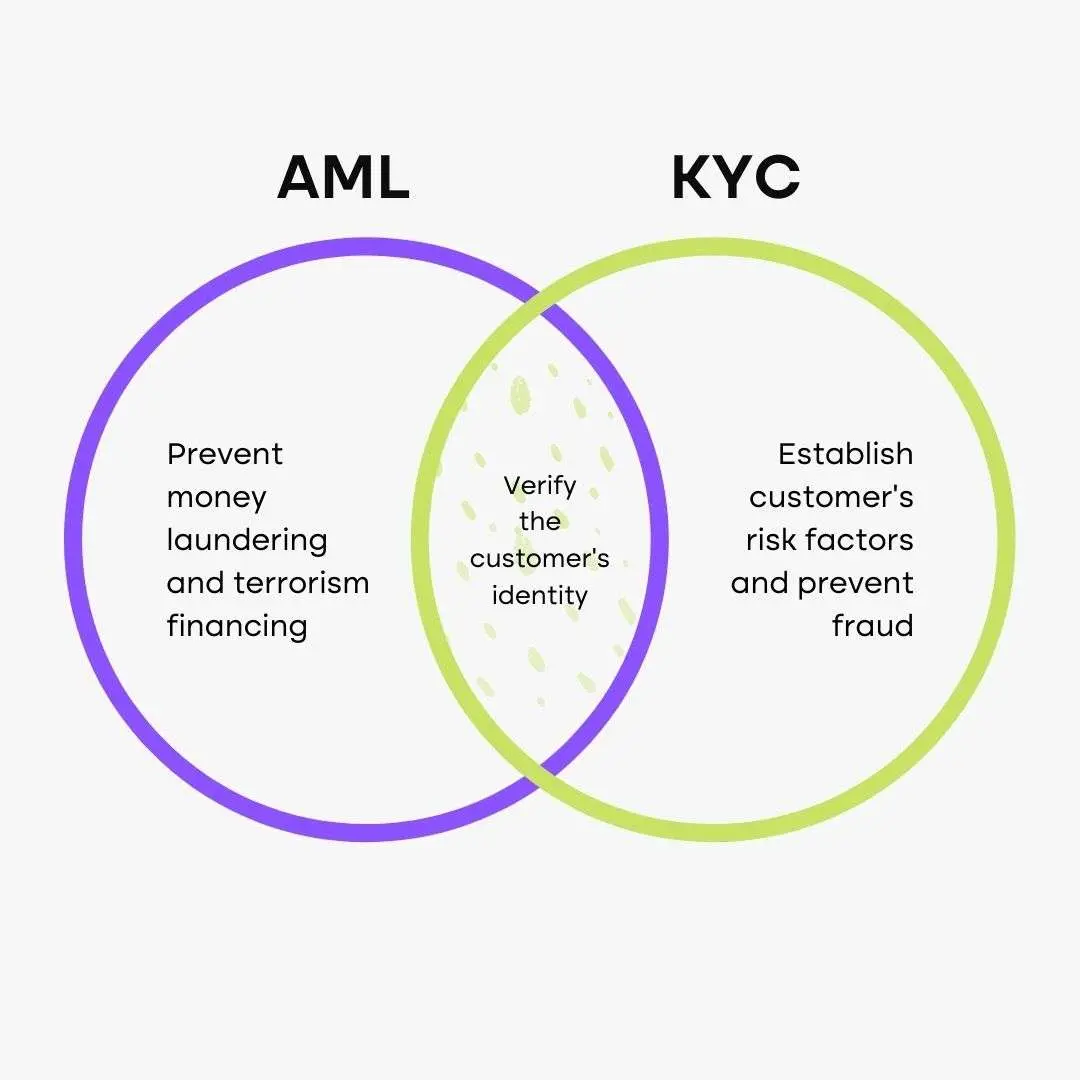
Differences Between KYC and AML
In addition to KYC, the definition of AML can often be seen on financial platforms. Some users mistakenly identify these concepts, but in reality, they differ.
What is AML?
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) is the principle of combating the laundering of money that could have been obtained by any criminal means. This procedure involves the identification, exchange, and storage of all information about the user, their income, exchanges between platforms, and other financial transactions.
Every financial organization today must also adhere to AML, as it helps to understand that their clients are not involved in illegal activities. An example of AML action is a suspicious transaction. If a user makes many transfers to different accounts in a short period, the financial organization can freeze the funds until all circumstances are clarified.
How Does AML Work?
As in the case of KYC, the AML procedure is also conducted in several stages:
-
Client identification. KYC and AML databases constantly exchange information, so this stage passes quickly;
-
Next, a risk assessment takes place: does the client have a criminal record, has he participated in corruption schemes, are there or were there links with suspicious organizations;
-
If the user is risky (a large businessman or a politician), then an additional check is carried out: business reputation, assets, sources of income, and connections are analyzed;
-
Next, the system begins to track all of the client's transactions between financial organizations. Noticing a suspicious transaction, AML can "freeze" the user's account for an indefinite period, and information about them is transferred to local financial regulators.
Main Differences
|
Criterion |
KYC (Know Your Customer) |
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) |
|
Definition |
Client identity verification |
Set of measures to prevent money laundering |
|
Goal |
Ensure the client is a real person or company |
Identify and block illegal financial operations |
|
Main Processes |
Document collection and verification (Passport, ID, registries) |
Transaction monitoring, identifying suspicious operations |
|
Relationship |
Part of the AML process |
Includes KYC but covers other measures as well |
|
Type of Check |
Initial check before starting work with a client |
Constant analysis of client operations |
|
Additional Stages |
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) – basic check |
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) – in-depth check for high-risk clients |
|
Responsibility |
Client provides accurate data |
Bank or financial organization must identify and report suspicious operations |
|
Regulators |
Compliance with internal and international standards |
Submission to financial regulators' requirements (e.g., FATF) |
|
Risks of Violation |
Fines, blocking of the client's account |
Legal liability, fines, loss of license |
Policies and Regulations in KYC
Compliance with KYC standards is not just a legal obligation for organizations, but a key tool in the fight against financial crimes. This process helps protect the financial system from illegal operations and increase its transparency. However, KYC requirements may vary depending on the country and field of activity.
Despite this, its main task remains unchanged – to ensure transparency and compliance with anti-money laundering norms. This is why KYC is a crucial element in the fight against financial fraud and the financing of criminal schemes.
If companies ignore KYC requirements, they risk facing serious consequences – from large fines to loss of business reputation. To avoid such risks, organizations must implement reliable KYC procedures that allow minimizing the likelihood of fraud and ensuring the security of financial operations.
Advantages of Digital KYC
With the development of technology, it has become possible to undergo the identity verification procedure remotely, that is, in a digital format, which is much more convenient for users. This approach has a number of advantages for both users and trading platforms:
-
KYC can be passed anywhere, time is not important, and a computer or smartphone will be required for this;
-
Thanks to the automation of processes, the entire procedure now takes much less time: some platforms confirm identity in 10-15 minutes;
-
Financial platforms save on remote identity confirmation: there is no need for additional personnel or physical movements, thereby reducing operational costs;
-
Clients react positively to organizations that allow them to pass KYC remotely, which forms a positive user experience.
Reasons for KYC Refusals
There are several main reasons why some people fail to pass the identity verification procedure, and they all come down to providing incomplete or unreliable data, namely:
-
If a client has provided incomplete or erroneous data, the financial organization cannot verify their identity;
-
Incorrect information about the source of income can lead to the platform being unable to correctly assess the risk associated with this client;
-
Legal entities must provide reliable information about their activities or structure. If this is not done, the company may be suspected of financial crimes;
-
Incorrect place of residence can also prevent a correct risk assessment.
If a user, when passing KYC, has made one of the mistakes described above, this can lead to the following consequences:
-
The financial organization may temporarily or completely refuse to provide its services to this client;
-
Loss of trust from the financial organization in the client;
-
If it is established that the client provided incorrect data on purpose (common among legal entities), this can be regarded as a financial crime;
-
Incorrect data leads to delays in operations.
Advantages of Optional KYC
We have already established that KYC makes life easier for both organizations and clients. However, it would be wrong not to analyze why optional identity confirmation also has a place:
-
Preservation of anonymity. Users can perform financial transactions without identity confirmation. This can currently be observed on decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges;
-
Reduction of costs for organizations by abandoning the identity confirmation procedure;
-
Platform users gain access to desired services much more easily, bypassing bureaucratic complexities;
-
A more flexible approach to security, as KYC works only when suspicious activity is noticed. Other protection mechanisms can conduct constant monitoring;
-
Financial organizations can be more responsible about meeting regulatory requirements, as if balancing between user convenience and legislative compliance.
Conclusion
The KYC procedure plays a key role in ensuring the security of financial platforms, preventing fraud, and complying with international anti-money laundering norms. Implementing effective KYC processes not only reduces the risks of illegal financial operations but also increases the trust of clients and regulators in the company.
Companies that ignore KYC requirements risk not only financial losses and fines but also a deterioration of reputation, which in the long term can lead to the loss of clients and even the closure of the business.
At the same time, platforms that implement advanced solutions (including Arbitrage Scanner for analyzing transaction patterns) gain a competitive advantage, providing clients not only with security but also with additional opportunities for profitable arbitrage in a regulated environment.
Thus, the competent implementation of KYC procedures is not just a legal obligation, but a strategic tool that helps financial organizations ensure security, trust, and stable development in the long term.
Want to learn more about crypto arbitrage?
Get a subscription and access the best tool on the market for arbitrage on Spot, Futures, CEX, and DEX exchanges.