What are funding rates in cryptocurrency?

with ArbitrageScanner!
Differences between perpetual and traditional futures
The first futures appeared in ancient Japan: rice sellers would agree in advance with buyers on the quantity of rice to be delivered on a certain date and at a set price. This arrangement benefited both parties:
- Sellers were assured their rice would be purchased at an agreed-upon price. While the price could rise, it could also fall.
- Buyers were guaranteed their rice supply and didn’t worry about it selling out.
Over time, futures became one of the derivative financial instruments in markets. Today, we have two types of futures: traditional and perpetual. Traditional futures are no different from those used in ancient Japan: they specify the quantity of the asset to be delivered, its price, and the expiration date (when the asset will be delivered and paid for).
Perpetual futures were created specifically for crypto trading by the BitMEX exchange in 2016. Essentially, a perpetual future is similar to a contract for difference (CFD), which first appeared in London in the early 1990s.
The main difference between traditional and perpetual futures is that a trader can hold the latter without an expiration date. When you buy a perpetual future, you automatically use leverage (even if it’s x1) and can hold the position as long as you have enough margin (funds on the exchange deposit).
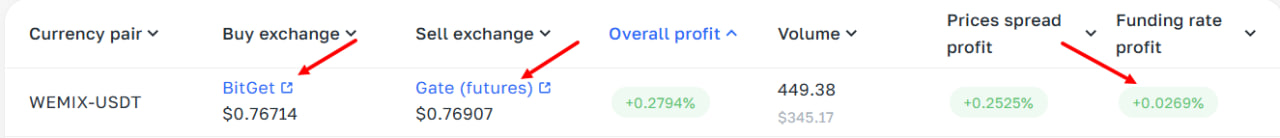
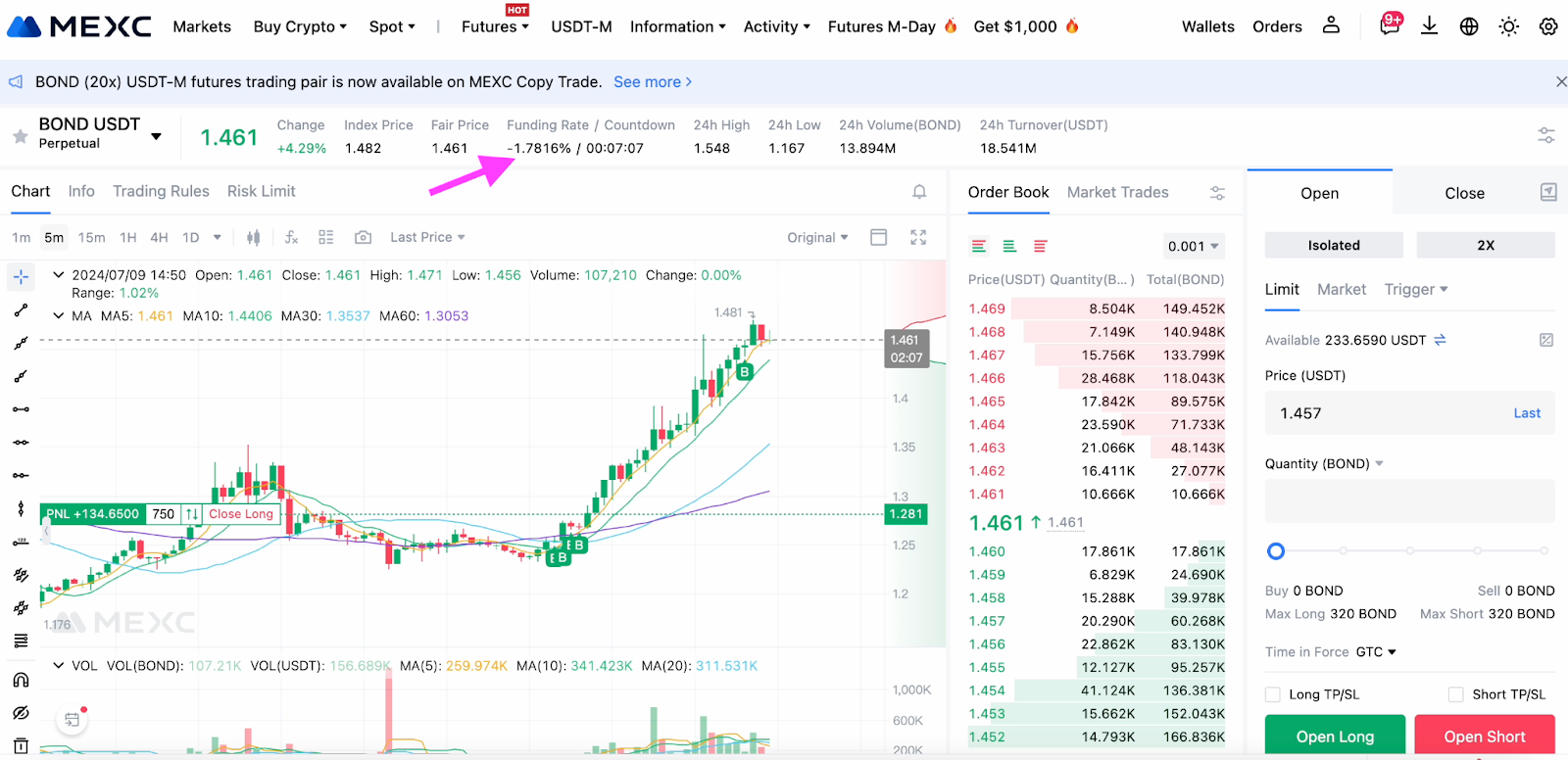
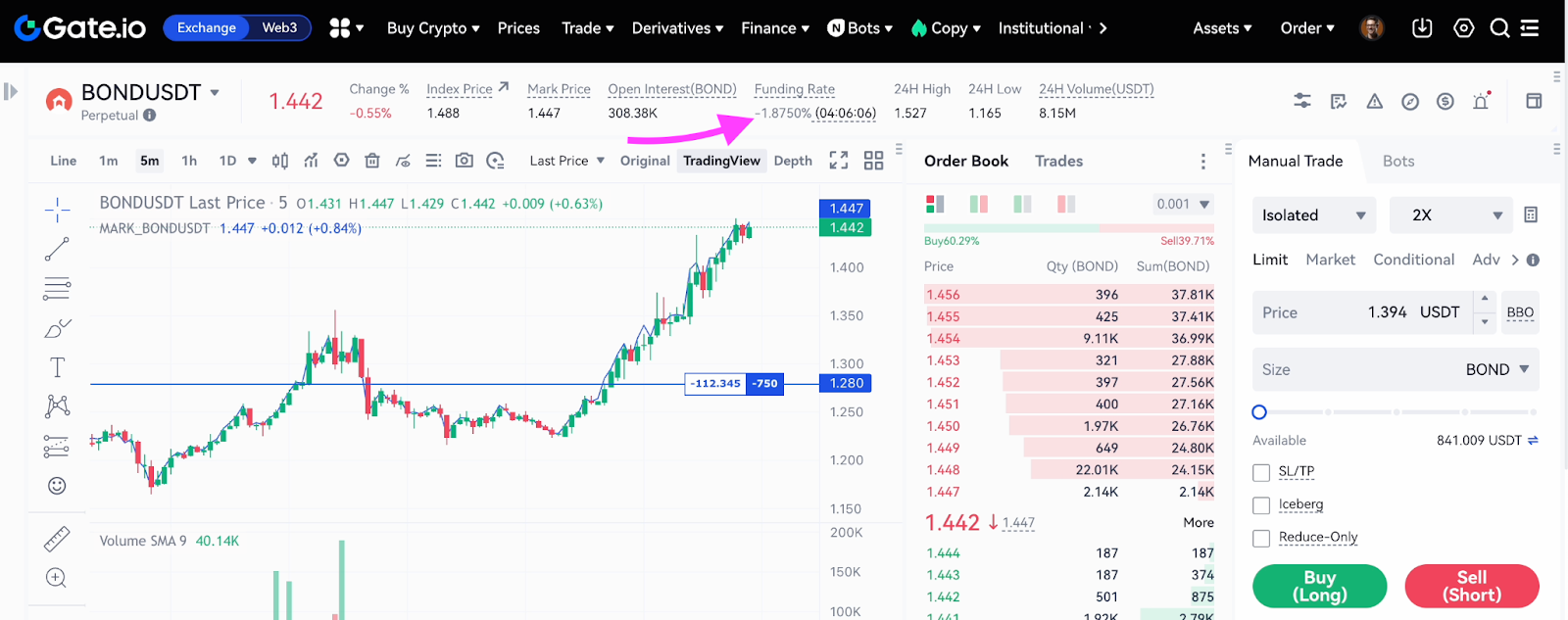
 Settlement for perpetual futures doesn’t occur in the traditional sense, so a mechanism is used to regularly align futures prices with the index (the average asset price across multiple spot markets) – this is called the funding rate or funding.
Settlement for perpetual futures doesn’t occur in the traditional sense, so a mechanism is used to regularly align futures prices with the index (the average asset price across multiple spot markets) – this is called the funding rate or funding.
What is funding?
Funding rates represent regular payments that traders with long or short positions either receive or pay based on the difference between spot market prices and perpetual futures market prices. A trader either receives or pays funding depending on the direction of their position.

The function of funding is to eliminate prolonged price discrepancies between these markets.
Funding rate formation
Want to learn more about crypto arbitrage?
Get a subscription and access the best tool on the market for arbitrage on Spot, Futures, CEX, and DEX exchanges.