Market Makers: Who They Are and How They Make Money

with ArbitrageScanner!
WHO IS A MARKET MAKER?
A market maker is a key player in the financial market, providing activity and liquidity. They are always ready to make a deal with any other market participant. Typically, market makers' activities are strictly regulated by law, although this has not yet been achieved in the cryptocurrency sector.
Every transaction requires a counterparty: if you want to sell an asset, you need a buyer, and vice versa. This is where market makers come into play, ensuring a constant presence of buyers and sellers for trading various instruments.
Types of Market Makers
Institutional
- Operate under strict regulatory rules
- Have contractual relationships with exchanges, where the obligations of the parties are specified
Speculative
- Operate in less regulated markets without a controlling body
FUNCTIONS OF MARKET MAKERS:
1) Providing Liquidity
- Thanks to market makers, market participants can always buy or sell an asset in the required volume.
- They prevent situations of insufficient demand or supply, which helps avoid wide spreads between bid and ask prices.
2) Maintaining Stable Prices
- Market makers prevent sharp price fluctuations.
- They ensure the constant presence of buy and sell orders, keeping prices close to the last trade, contributing to price stability.
To fulfill their functions, market makers perform the following tasks:
1) Maintaining Two-Way Quotes: They post bid and ask prices for a certain volume. This ensures there is always someone to trade with, maintaining market liquidity.
2) Keeping the Spread Stable: They keep the difference between bid and ask prices (spread) stable. For example, a spread of $5-10 for the ETH/USDT pair, which prevents sharp price fluctuations.
!!! NOTE: The spread range mentioned above is an example. We do not know the exact figures. Consider this in your work.
HOW MARKET MAKERS EARN
1) Exchange Fees: Institutional market makers receive commissions from the exchange for their services;
2) Spread: Profit from the difference between bid and ask prices;
3) Turnover: To maintain market stability, market makers place many orders, satisfying both buyers and sellers. Acting as a bridge to increase turnover.
ADVANTAGE OF A MARKET MAKER OVER OTHER MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Market makers not only see current prices but also volumes, margin zones (Fig. 1), liquidations (Fig. 2), the full order book (Fig. 3), stop-losses, and take-profits. Even in real-time, market makers can see how you adjust your positions. Using insider information for decision-making, market makers can provide it to a certain circle of people.
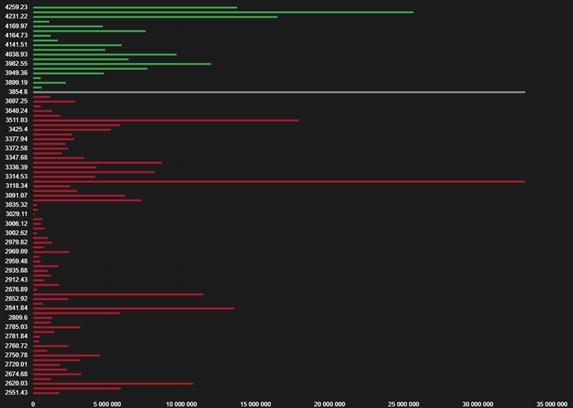
Fig. 1 – “Example of Margin Zones by Market Makers”
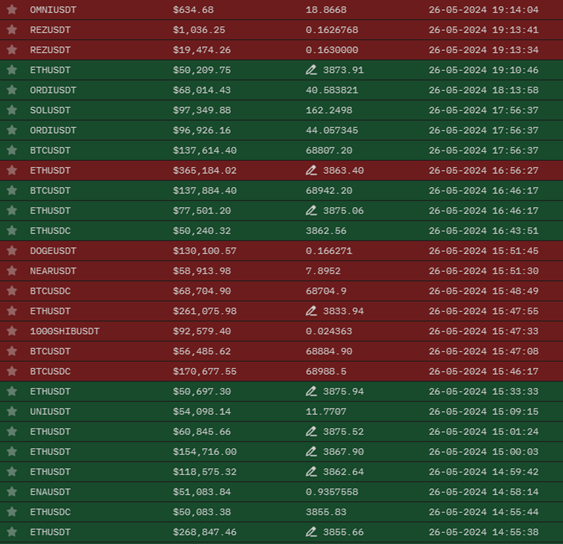
Fig. 2 – “Example of Liquidations and Position Adjustments Seen by Market Makers”
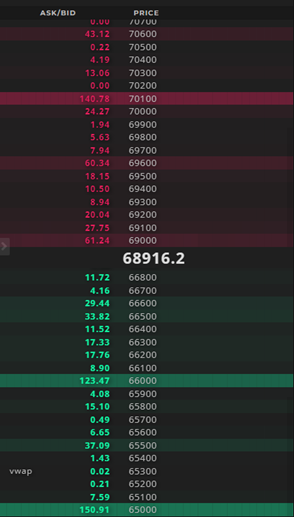
Fig. 3 – “Full Order Book by Market Maker for BTC/USDT 1D on Binance Exchange”
Is it true that market makers are a necessary evil?
This statement is harsh and incorrect. A market maker primarily creates comfortable conditions for market participants: sellers and buyers. By applying their algorithms, they earn on price movements by providing liquidity.
Want to learn more about crypto arbitrage?
Get a subscription and access the best tool on the market for arbitrage on Spot, Futures, CEX, and DEX exchanges.